Using RSTUF
Assuming a successful Repository Service for TUF (RSTUF) Deployment and Service Setup is complete, these are the usage:
Adding/Removing artifacts to TUF Metadata
RSTUF allows organizations to easily integrate the robust TUF metadata along the existing content repositories using the RSTUF API.
Adding or removing artifacts to the content repository to protect the user must be added to TUF metadata, enabling the TUF Client to fetch the new artifact using the trusted metadata.
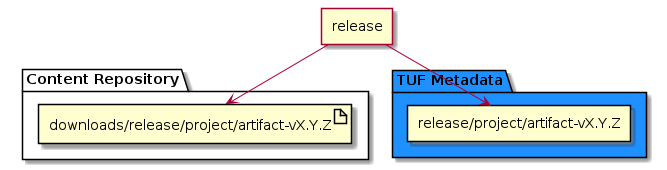
Releasing the artifact in the content repository does not require changes to the existing process.
To manage artifacts in the TUF metadata, use HTTP requests to the RSTUF API. The main actions are adding or removing artifacts to the metadata.
A successful RSTUF deployment will have an RSTUF HTTP(S) API service
http://<IP ADDRESS>/api/v1/
Adding artifacts
Send requests to http://<IP ADDRESS>/api/v1/artifacts with method POST
with a JSON payload.
Note
See the complete API documentation
This payload supports one or multiple artifacts (targets)
Add artifacts payload
1{
2 "targets": [
3 {
4 "info": {
5 "length": "<LENGTH>",
6 "hashes": {
7 "<HASH-NAME>": "<HASH>"
8 },
9 },
10 "path": "<PATH>"
11 }
12 ]
13}
Parameters |
Details |
Example |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The hash output, such as |
|
|
The full artifact path, excluding the Base URL. If clients will
look for artifacts in
|
|
Removing artifacts
Send requests to http://<IP ADDRESS>/api/v1/artifacts/delete with method POST
with a JSON payload.
Note
See the complete API documentation
This payload supports one or multiple artifacts
Remove artifacts payload
1{
2 "targets": ["<PATH>"]
3}
Parameters |
Details |
Example |
|---|---|---|
|
The full artifact path, excluding the Base URL. If clients will
look for artifacts in
|
|
Advanced Usage
Managing adding/removing artifacts tasks – call-backs
Adding/removing artifacts to Repository Service for TUF (RSTUF) is an asynchronous process.
Submitting a request for adding/removing will return an HTTP status code 202,
meaning the task is submitted. As part of the body, there is the task id.
Response body adding/removing targets, task id:
{
"data": {
"task_id": "<TASK ID>",
},
}
This body has more details such as targets, last_update, etc. See the endpoint response documentation
To retrieve the task status, send requests to
http://<IP ADDRESS>/api/v1/task?task_id=<TASK ID> with method
GET.
The response will have a body with all task details
{
"data": {
"task_id": "<TASK ID>",
"state": "<STATE>",
"result": {
"status": "Task finished.",
"details": {
"key": "value"
}
}
},
"message": "Task state."
}
See the endpoint task documentation for more details.
Adding artifacts for back-signing
Repository Service for TUF (RSTUF) allows adding artifacts without publishing immediately to the TUF Metadata.
As example, an organization adds and removes artifacts while batch publishing daily.
This feature requires adding the publish_targets parameter to
Add artifacts payload or
Remove artifacts payload.
Examples:
Adding artifacts without publishing
1{
2 "targets": [
3 {
4 "info": {
5 "length": "<LENGTH>",
6 "hashes": {
7 "<HASH-NAME>": "<HASH>"
8 },
9 },
10 "path": "<PATH>"
11 }
12 ],
13 "publish_targets": false
14}
Removing artifacts without publishing
1{
2 "targets": ["<PATH>"],
3 "publish_targets": false
4}
To publish all artifacts added/removed without publishing, send a request to
http://<IP ADDRESS>/api/v1/targets/publish with method POST.
Note
See the complete API documentation
Recovering a compromised key
The Repository Service for TUF (RSTUF) can help to replace the compromised keys.
If an offline (Root) key is compromised (a threshold of keys belonging to the metadata to the Root metadata) is required a Metadata Update.
If the online key is compromised, it requires a Metadata Update to replace the online key.
Metadata Update
The Metadata Update ceremony is a guided process allowing you to:
add or remove key(s)
change the Root role key threshold
change the Root expiration
Before starting the Metadata Update Ceremony authorization is required with at least one private root key to be fully loaded.
The changes a user is allowed to make are not limited to the Root role, but also include the keys used by all other roles as well.
When the ceremony is complete, the CLI can send the new information directly to an RSTUF API instance or save it locally into a JSON file.
The Metadata Update ceremony could be used for multiple use cases as for example:
recover from a compromised key
remove a key for a person leaving the organization
add a new key to be used by a new employee
improve the security of a repository by increasing the Root role threshold
Importing existing targets
When adopting Repository Service for TUF (RSTUF), with a large number of targets (artifacts/packages/files/etc.), using the “import targets” feature is recommended.
Existing targets can be sent using the REST API, however it will be slower than using the “import targets” feature.
The “import targets” feature can be used to add targets directly to the RSTUF database skipping the standard processing of the API. Normally, when adding a target through the API there will be an overhead of multiple additional operations which for a large number of targets can prove to be significant.
Below are sample benchmarks of the “import targets” feature:
Running in a Macbook Pro (2019) 2,4 GHz 8-Core Intel Core i9/32GB 2667 MHz DDR4:
- Adding 500,000 targets: ~40 minutes
Loaded 1 of 1 file with 500,000 targets
- Adding 1,000,000 targets: ~55 minutes
Loaded 1 of 2 file with 500,000 targets
Loaded 2 of 2 file with 500,000 targets
Warning
Use the API flow integration to the release process (CI/CD or Distribution Platform).
Do not use “import targets” as a replacement for the standard procedure to add targets throughout the RSTUF API or CLI tool after RSTUF is deployed. This feature should only be used before going live with RSTUF.
RSTUF-CLI contains the guide/repository-service-tuf-cli/index:Import Targets (``import-targets``) feature.
CLI usage
Import Artifacts (import-artifacts)
This feature imports a large number of artifacts directly to RSTUF Database. RSTUF doesn’t recommend using this feature for regular flow, but in case you’re onboarding an existent repository that contains a large number of artifacts.
This feature requires extra dependencies:
pip install repository-service-tuf[psycopg2,sqlachemy]
To use this feature, you need to create CSV files with the content to be imported by RSTUF CLI.
This content requires the following data:
path: The target path
size: The target size
hash-type: The defined hash as a metafile. Example: blak2b-256
hash: The hash
The CSV must use a semicolon as the separator, following the format
path;size;hash-type;hash without a header.
See the below CSV file example:
relaxed_germainv1.tar.gz;12345;blake2b-256;716f6e863f744b9ac22c97ec7b76ea5f5908bc5b2f67c61510bfc4751384ea7a
vigilant_keldyshv2.tar.gz;12345;blake2b-256;716f6e863f744b9ac22c97ec7b76ea5f5908bc5b2f67c61510bfc4751384ea7a
adoring_teslav3.tar.gz;12345;blake2b-256;716f6e863f744b9ac22c97ec7b76ea5f5908bc5b2f67c61510bfc4751384ea7a
funny_greiderv4.tar.gz;12345;blake2b-256;716f6e863f744b9ac22c97ec7b76ea5f5908bc5b2f67c61510bfc4751384ea7a
clever_ardinghelliv5.tar.gz;12345;blake2b-256;716f6e863f744b9ac22c97ec7b76ea5f5908bc5b2f67c61510bfc4751384ea7a
pbeat_galileov6.tar.gz;12345;blake2b-256;716f6e863f744b9ac22c97ec7b76ea5f5908bc5b2f67c61510bfc4751384ea7a
wonderful_gangulyv7.tar.gz;12345;blake2b-256;716f6e863f744b9ac22c97ec7b76ea5f5908bc5b2f67c61510bfc4751384ea7a
sweet_ardinghelliv8.tar.gz;12345;blake2b-256;716f6e863f744b9ac22c97ec7b76ea5f5908bc5b2f67c61510bfc4751384ea7a
brave_mendelv9.tar.gz;12345;blake2b-256;716f6e863f744b9ac22c97ec7b76ea5f5908bc5b2f67c61510bfc4751384ea7a
nice_ridev10.tar.gz;12345;blake2b-256;716f6e863f744b9ac22c97ec7b76ea5f5908bc5b2f67c61510bfc4751384ea7a
❯ rstuf admin import-artifacts -h
Usage: rstuf admin import-artifacts [OPTIONS]
Import artifacts to RSTUF from exported CSV file.
╭─ Options ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
│ --api-server TEXT RSTUF Metadata URL i.e.: http://127.0.0.1 . [required] │
│ * --db-uri TEXT RSTUF DB URI. i.e.: postgresql://postgres:secret@127.0.0.1:5433 [required] │
│ * --csv TEXT CSV file to import. Multiple --csv parameters are allowed. See rstuf CLI guide for more details. [required] │
│ --skip-publish-artifacts Skip publishing artifacts in TUF Metadata. │
│ --help -h Show this message and exit. │
╰─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
❯ rstuf admin import-artifacts --db-uri postgresql://postgres:secret@127.0.0.1:5433 --csv artifacts-1of2.csv --csv artifacts-2of2.csv --metadata-url http://127.0.0.1:8080/
Import status: Loading data from ../repository-service-tuf/tests/data/artifacts-1of2.csv
Import status: Importing ../repository-service-tuf/tests/data/artifacts-1of2.csv data
Import status: ../repository-service-tuf/tests/data/artifacts-1of2.csv imported
Import status: Loading data from ../repository-service-tuf/tests/data/artifacts-2of2.csv
Import status: Importing ../repository-service-tuf/tests/data/artifacts-2of2.csv data
Import status: ../repository-service-tuf/tests/data/artifacts-2of2.csv imported
Import status: Commiting all data to the RSTUF database
Import status: All data imported to RSTUF DB
Import status: Submitting action publish artifacts
Import status: Publish artifacts task id is dd1cbf2320ad4df6bda9ca62cdc0ef82
Import status: task STARTED
Import status: task SUCCESS
Import status: Finished.
Note
When providing users with download or update capabilities, it is necessary to add signed metadata checkpoints to the functionality tools.